A Simple Guide to Creating Responsive HTML Tables
In modern web development, responsive HTML tables are crucial for maintaining usability across different screen sizes. Tables often present challenges on smaller screens due to their rigid structure. This guide covers multiple techniques to make HTML tables responsive, including horizontal scrolling, column hiding, row collapsing, and advanced layout strategies using Flexbox and Grid. Each method includes practical examples to help you implement them effectively.
Why Responsive Tables Matter
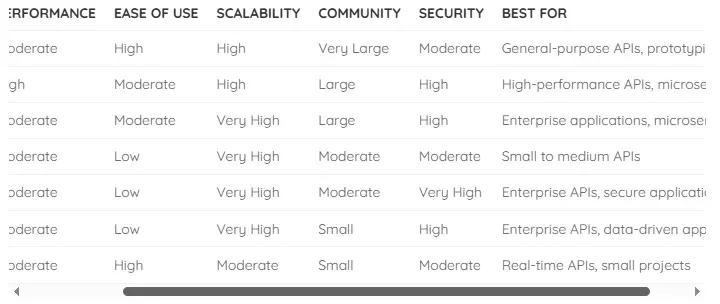
Tables are commonly used for displaying structured data like pricing plans, schedules, or comparisons. On mobile devices, tables can become difficult to read or navigate. A responsive table adapts to the screen size, preserving readability and improving user experience.
1. Horizontal Scrolling with CSS Overflow
The simplest responsive table technique is wrapping the table in a container with overflow-x: auto, allowing horizontal scrolling.
CSS
12345678.table-container { overflow-x: auto; max-width: 100%; } .table-container table { width: max-content; border-collapse: collapse; }
HTML
1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526<div class="table-container"> <table> <thead> <tr> <th>Name</th> <th>Age</th> <th>Occupation</th> <th>Location</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr> <td>Ravi Sankar</td> <td>30</td> <td>Developer</td> <td>India</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Jane Smith</td> <td>25</td> <td>Designer</td> <td>US</td> </tr> </tbody> </table> </div>
Pros
- Simple to implement
- Retains full table structure
- Suitable for wide tables
Cons
- Horizontal scroll may affect usability
- Doesn’t restructure content
2. Hiding Columns on Smaller Screens
Use CSS media queries to hide less-important columns on small screens.
CSS
12345@media screen and (max-width: 600px) { .hide-on-mobile { display: none; } }
HTML
123456789101112131415161718192021222324<table> <thead> <tr> <th>Name</th> <th>Age</th> <th class="hide-on-mobile">Occupation</th> <th class="hide-on-mobile">Location</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr> <td>Ravi Sankar</td> <td>30</td> <td class="hide-on-mobile">Developer</td> <td class="hide-on-mobile">India</td> </tr> <tr> <td>Jane Smith</td> <td>25</td> <td class="hide-on-mobile">Designer</td> <td class="hide-on-mobile">US</td> </tr> </tbody> </table>
Pros
- Removes clutter on small screens
- Maintains basic structure
Cons
- Information loss if hidden columns are important
3. Collapsing Rows into Stacked Cards
Transform rows into card-style blocks using display: block and data-label attributes.
CSS
12345678910111213141516171819202122232425@media screen and (max-width: 600px) { table, thead, tbody, th, td, tr { display: block; } thead { display: none; } tr { margin-bottom: 15px; border: 1px solid #ddd; padding: 10px; } td { position: relative; padding-left: 50%; text-align: left; } td:before { content: attr(data-label); position: absolute; left: 10px; width: 45%; font-weight: bold; } }
HTML
123456789101112131415161718192021222324<table> <thead> <tr> <th>Name</th> <th>Age</th> <th>Occupation</th> <th>Location</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr> <td data-label="Name">Ravi Sankar</td> <td data-label="Age">30</td> <td data-label="Occupation">Developer</td> <td data-label="Location">India</td> </tr> <tr> <td data-label="Name">Jane Smith</td> <td data-label="Age">25</td> <td data-label="Occupation">Designer</td> <td data-label="Location">US</td> </tr> </tbody> </table>
Pros
- Mobile-friendly
- Clear content structure
Cons
- Requires
data-labelattributes
4. Flexbox for Wrapping Cells
Flexbox can wrap cells dynamically within a responsive container.
CSS
1234567891011121314151617.table-container { display: flex; flex-wrap: wrap; } table { flex: 1 1 100%; } th, td { flex: 1 1 25%; padding: 10px; border: 1px solid #ddd; } @media screen and (max-width: 600px) { th, td { flex: 1 1 50%; } }
Pros
- Responsive and flexible
- All content remains visible
Cons
- Less control over exact dimensions
5. Collapsible Rows with JavaScript
Toggle visibility of row details with buttons and JS.
HTML & JS
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536373839404142<table> <thead> <tr> <th>Name</th> <th>Age</th> <th>Details</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody> <tr> <td>Ravi Sankar</td> <td>30</td> <td> <button onclick="toggleDetails(this)">Show Details</button> <div class="details" style="display: none;"> <p>Occupation: Developer</p> <p>Location: India</p> </div> </td> </tr> <tr> <td>Jane Smith</td> <td>25</td> <td> <button onclick="toggleDetails(this)">Show Details</button> <div class="details" style="display: none;"> <p>Occupation: Designer</p> <p>Location: US</p> </div> </td> </tr> </tbody> </table> <script> function toggleDetails(button) { const details = button.nextElementSibling; const isHidden = details.style.display === 'none'; details.style.display = isHidden ? 'block' : 'none'; button.textContent = isHidden ? 'Hide Details' : 'Show Details'; } </script>
CSS
1234.details { padding: 10px; background: #f9f9f9; }
Pros
- Interactive and space-saving
Cons
- Requires JavaScript
6. CSS Grid for Custom Layouts
CSS Grid provides precision and adaptability in layout design.
CSS
123456789101112.table-container { display: grid; grid-template-columns: repeat(auto-fit, minmax(100px, 1fr)); gap: 10px; } table { display: contents; } th, td { border: 1px solid #ddd; padding: 10px; }
Pros
- High flexibility
- Ideal for complex responsive designs
Cons
- Requires modern browser support
Best Practices
- Prioritize Key Content on small screens
- Test Responsiveness across all devices
- Maintain Accessibility using semantic HTML and ARIA attributes
- Optimize Performance by minimizing JS and CSS bloat
- Use Clear Visual Styling for readability and UX
Conclusion
Responsive tables are a vital part of modern web design. Depending on your data and use case, you can choose from simple overflow techniques to more advanced layouts using CSS Grid and JavaScript. Combining these strategies allows you to create adaptable and user-friendly data displays across all devices.